Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMSC4A7)
| Drug Name |
Indomethacin
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Aconip; Amuno; Arthrexin; Artracin; Artrinovo; Artrivia; Bonidin; Bonidon; Catlep; Confortid; Dolcidium; Dolovin; Durametacin; Elmetacin; Hicin; IMN; Idomethine; Imbrilon; Inacid; Indacin; Indameth; Indmethacine; Indocid; Indocin; Indomecol; Indomed; Indomee; Indometacin; Indometacina; Indometacine; Indometacinum; Indometacyna; Indomethacine; Indomethacinum; Indomethancin; Indomethazine; Indomethegan; Indomethine; Indometicina; Indomo; Indomod; Indoptic; Indoptol; Indorektal; Indoxen; Inflazon; Infrocin; Lausit; Liometacen; Metacen; Metartril; Methazine; Metindol; Mezolin; Miametan; Mikametan; Mobilan; Novomethacin; Reumacide; Sadoreum; Tannex; Vonum; Bonidon Gel; DESMETHYL INDOMETHACIN; Dolcidium PL;Flexin continus; Indocid Pda; Indocid Sr; Indocin Sr; Indolar SR; Indometacyna [Polish]; Indometicina [Spanish]; Inteban sp; Rhemacin LA; Rheumacin LA; I 7378; IN1454; Indomet 140; Aconip (TN); Apo-Indomethacin; Chibro-amuno; Chrono-indicid; Chrono-indocid; Indo-Lemmon; Indo-Spray; Indo-phlogont; Indo-rectolmin; Indo-tablinen; Indocid (TN); Indocid (pharmaceutical); Indocin (TN); Indocin I.V; Indometacina [INN-Spanish]; Indometacine [INN-French]; Indometacinum [INN-Latin]; Indomethacin (USP); Indomethacin [USAN:BAN]; Novo-Methacin; Indochron E-R (TN); Indocin I.V.; Indocin-SR (TN); Indometacin (JP15/INN); Indomethacin & MAP-30; Indomethacin, Indochron E-R, Indocin-SR, Indocid, Indocin, Indomethacin
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiinflammatory Agents
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
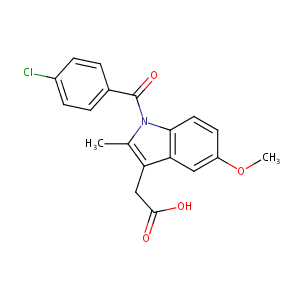 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 357.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 4.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Bursitis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Indomethacin
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Indomethacin (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Indomethacin FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | ||||
| 3 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04344457) Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Oral Hydroxychloroquine, Indomethacin and Zithromax in Subjects With Mild Symptoms of COVID-19. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | ||||
| 4 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 5 | Critical Evaluation of Human Oral Bioavailability for Pharmaceutical Drugs by Using Various Cheminformatics Approaches | ||||
| 6 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 7 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 8 | ADReCS-Target: target profiles for aiding drug safety research and application. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 4;46(D1):D911-D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx899. | ||||
| 9 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | ||||
| 10 | Indomethacin induces apoptosis via a MRP1-dependent mechanism in doxorubicin-resistant small-cell lung cancer cells overexpressing MRP1. Br J Cancer. 2007 Oct 22;97(8):1077-83. | ||||
| 11 | Substrates, inducers, inhibitors and structure-activity relationships of human Cytochrome P450 2C9 and implications in drug development. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(27):3480-675. | ||||
| 12 | Contribution of UDP-glucuronosyltransferases 1A9 and 2B7 to the glucuronidation of indomethacin in the human liver. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2007 Mar;63(3):289-96. | ||||
| 13 | Prostaglandins and leukotriene B4 are potent inhibitors of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 activity in human choriocarcinoma JEG-3 cells. Biol Reprod. 1999 Jul;61(1):40-5. | ||||
| 14 | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs induce colorectal cancer cell apoptosis by suppressing 14-3-3epsilon. Cancer Res. 2007 Apr 1;67(7):3185-91. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3431. | ||||
| 15 | 15-Hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-PGDH) is up-regulated by flurbiprofen and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in human colon cancer HT29 cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2009 Jul 15;487(2):139-45. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2009.05.017. Epub 2009 Jun 6. | ||||
| 16 | Indomethacin stimulates activity and expression of ecto-5'-nucleotidase/CD73 in glioma cell lines. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Aug 13;569(1-2):8-15. | ||||
| 17 | Mechanisms of indomethacin-induced alterations in the choline phospholipid metabolism of breast cancer cells. Neoplasia. 2006 Sep;8(9):758-71. | ||||
| 18 | Evaluation of developmental toxicity using undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells. J Appl Toxicol. 2015 Feb;35(2):205-18. | ||||
| 19 | Drug-induced hepatic steatosis in absence of severe mitochondrial dysfunction in HepaRG cells: proof of multiple mechanism-based toxicity. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2021 Apr;37(2):151-175. doi: 10.1007/s10565-020-09537-1. Epub 2020 Jun 14. | ||||
| 20 | Novis BH, Korzets Z, Chen P, Bernheim J "Nephrotic syndrome after treatment with 5-aminosalicylic acid." Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 296 (1988): 1442. [PMID: 3132281] | ||||
| 21 | Buchman AL, Schwartz MR "Colonic ulceration associated with the systemic use of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory medication." J Clin Gastroenterol 22 (1996): 224-6. [PMID: 8724264] | ||||
| 22 | EMEA "EMEA public statement on leflunomide (ARAVA) - severe and serious hepatic reactions.". | ||||
| 23 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 24 | Abad S, Moachon L, Blanche P, Bavoux F, Sicard D, Salmon-Ceron D "Possible interaction between glicazide, fluconazole and sulfamethoxazole resulting in severe hypoglycaemia." Br J Clin Pharmacol 52 (2001): 456-7. [PMID: 11678792] | ||||
| 25 | Product Information. Aubagio (teriflunomide). Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 26 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Sirturo (bedaquiline). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 28 | Product Information. Acular (ketorolac). Allergan Inc, Irvine, CA. | ||||
| 29 | Product Information. Factive (gemifloxacin). GeneSoft Inc, San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 30 | Assael BM, Chiabrando C, Gagliardi L, Noseda A, Bamonte F, Salmona M "Prostaglandins and aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity." Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 78 (1985): 386-94. [PMID: 4049389] | ||||
| 31 | Product Information. Actonel (risedronate). Procter and Gamble Pharmaceuticals, Cincinnati, OH. | ||||
| 32 | Product Information. Turalio (pexidartinib). Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Parsippany, NJ. | ||||
| 33 | Product Information. Piqray (alpelisib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 34 | Wong GT, Lee EY, Irwin MG. Contrast induced nephropathy in vascular surgery.?Br J Anaesth. 2016;117 Suppl 2:ii63-ii73. [PMID: 27566809] | ||||
| 35 | Alderman CP, Moritz CK, Ben-Tovim DI "Abnormal platelet aggregation associated with fluoxetine therapy." Ann Pharmacother 26 (1992): 1517-9. [PMID: 1482806] | ||||
| 36 | Product Information. Eloxatin (oxaliplatin). Sanofi Winthrop Pharmaceuticals, New York, NY. | ||||
| 37 | Product Information. Yasmin (drospirenone-ethinyl estradiol) Berlex Laboratories, Richmond, CA. | ||||
| 38 | Bang CJ, Riedel B, Talstad I, Berstad A "Interaction between heparin and acetylsalicylic acid on gastric mucosal and skin bleeding in humans." Scand J Gastroenterol 27 (1992): 489-94. [PMID: 1321488] | ||||
| 39 | Product Information. Korlym (mifepristone). Corcept Therapeutics Incorporated, Menlo Park, CA. | ||||
| 40 | Product Information. Kalydeco (ivacaftor). Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 41 | Product Information. Vistide (cidofovir). Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. | ||||
| 42 | Product Information. Prevymis (letermovir). Merck & Company Inc, Whitehouse Station, NJ. | ||||
| 43 | Product Information. Xarelto (rivaroxaban). Bayer Inc, Toronto, IA. | ||||
| 44 | Product Information. Emend (aprepitant). Merck & Company Inc, West Point, PA. | ||||
| 45 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 46 | Muller FO, Schall R, Devaal AC, Groenewoud G, Hundt HKL, Middle MV "Influence of meloxicam on furosemide pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in healthy volunteers." Eur J Clin Pharmacol 48 (1995): 247-51. [PMID: 7589049] | ||||
| 47 | Abdel-Haq B, Magagna A, Favilla S, Salvetti A "Hemodynamic and humoral interactions between perindopril and indomethacin in essential hypertensive subjects." J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 18 (1991): s33-6. [PMID: 1725198] | ||||
| 48 | Product Information. Priftin (rifapentine). Hoechst Marion-Roussel Inc, Kansas City, MO. | ||||
| 49 | Product Information. Adcetris (brentuximab vedotin). Seattle Genetics Inc, Bothell, WA. | ||||
| 50 | Elsharkawy AM, Schwab U, McCarron B, et al. "Efavirenz induced acute liver failure requiring liver transplantation in a slow drug metaboliser." J Clin Virol 58 (2013): 331-3. [PMID: 23763943] | ||||
| 51 | Product Information. Intelence (etravirine). Ortho Biotech Inc, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 52 | Product Information. Norvir (ritonavir). Abbott Pharmaceutical, Abbott Park, IL. | ||||
| 53 | Product Information. Kynamro (mipomersen). Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 54 | Product Information. Juxtapid (lomitapide). Aegerion Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 55 | McCarthy JT, Torres VE, Romero JC, et al "Acute intrinsic renal failure induced by indomethacin." Mayo Clin Proc 57 (1982): 289-96. [PMID: 6952058] | ||||
| 56 | Product Information. Potassium Chloride ER (potassium chloride). Zydus Pharmaceuticals (USA) Inc, Princeton, NJ. | ||||
| 57 | Adams JD, Hunter GA "Drug interaction in psoriasis." Australas J Dermatol 17 (1976): 39-40. [PMID: 1022213] | ||||
| 58 | Blakely KM, Drucker AM, Rosen CF "Drug-induced photosensitivity-an update: Culprit drugs, prevention and management." Drug Saf 42 (2019): 827-47. [PMID: 30888626] | ||||
| 59 | Caruso V, Iacoviello L, Di Castelnuovo A, et.al "Thrombotic complications in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a meta-analysis of 17 prospective studies comprising 1752 pediatric patients." Blood 108 (2006): 2216-22. [PMID: 16804111] | ||||
| 60 | Product Information. Zydelig (idelalisib). Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. | ||||
| 61 | Product Information. Calquence (acalabrutinib). Astra-Zeneca Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 62 | Agencia Espaola de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios Healthcare "Centro de informacion online de medicamentos de la AEMPS - CIMA.". | ||||
| 63 | Product Information. Iclusig (ponatinib). Ariad Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 64 | Product Information. Exjade (deferasirox). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 65 | Product Information. Gleevec (imatinib mesylate). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 66 | Product Information. Sprycel (dasatinib). Bristol-Myers Squibb, Princeton, NJ. | ||||
| 67 | Product Information. Brukinsa (zanubrutinib). BeiGene USA, Inc, San Mateo, CA. | ||||
| 68 | Product Information. Zontivity (vorapaxar). Merck & Company Inc, Whitehouse Station, NJ. | ||||
| 69 | Product Information. Integrilin (eptifibatide). Schering Laboratories, Kenilworth, NJ. | ||||
| 70 | Product Information. Solaraze (diclofenac topical). Doak Dermatologics Division, Fairfield, NJ. | ||||
| 71 | EMA. European Medicines Agency. European Union "EMA - List of medicines under additional monitoring.". | ||||
| 72 | Concomitant use of ibuprofen and aspirin. J Pain Palliat Care Pharmacother 21 (2007): 73-4. [PMID: 17844731] | ||||
| 73 | Benoist G, van Oort I, et al "Drug-drug interaction potential in men treated with enzalutamide: Mind the gap." Br J Clin Pharmacol 0 (2017): epub. [PMID: 28881501] | ||||
| 74 | Product Information. Tracleer (bosentan). Acetelion Pharmaceuticals US, Inc, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 75 | Product Information. Flolan (epoprostenol). Glaxo Wellcome, Research Triangle Park, NC. | ||||
| 76 | Product Information. Prograf (tacrolimus). Fujisawa, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
| 77 | Webberley MJ, Murray JA "Life-threatening acute hyponatraemia induced by low dose cyclophosphamide and indomethacin." Postgrad Med J 65 (1989): 950-2. [PMID: 2616440] | ||||
| 78 | Product Information. ReVia (naltrexone). DuPont Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 79 | Product Information. Cometriq (cabozantinib). Exelixis Inc, S San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 80 | Product Information. Bevyxxa (betrixaban). Portola Pharmaceuticals, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
